NASA has awarded payload flight opportunities for research and technology development onboard the International Space Station to academic institutions across the U.S. Among the selected projects is the launch and deployment of the KySat-2 secondary model from the ISS. The primary model KySat-2 was launched by NASA on November 19, 2013 out of Wallops Island, VA.
 The research experiment includes several systems and experiments designed by Dr. Rawashdeh at the Space Systems Laboratory at the University of Kentucky. Specifically, a flight test of the Stellar Gyroscope concept, and analysis and of attitude dynamics using the SNAP simulation tool. The Rawashdeh group at UM-Dearborn will continue to support the mission, mainly in analyzing the experiment data. More on the KySat-2 Mission can be found here.
The research experiment includes several systems and experiments designed by Dr. Rawashdeh at the Space Systems Laboratory at the University of Kentucky. Specifically, a flight test of the Stellar Gyroscope concept, and analysis and of attitude dynamics using the SNAP simulation tool. The Rawashdeh group at UM-Dearborn will continue to support the mission, mainly in analyzing the experiment data. More on the KySat-2 Mission can be found here.
The awards are through NASA’s Experimental Program to Stimulate Competitive Research (EPSCoR). The official press release can be found here, with abstracts here.
Abbreviated abstract:
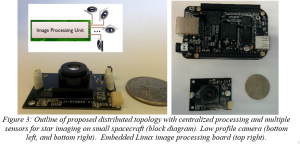
The primary mission is to test a new method of attitude determination for small spacecraft called the stellar gyroscope, which estimates attitude changes by analyzing the relative motion of stars between successive image frames, lowering the computational and power requirements necessary to propagate attitude changes. Launch from the ISS will allow characterization the stellar gyroscope hardware, verification of the sensitivity of the sensor for star imaging as well as the image processing required on-orbit. Additionally, ejection from the ISS altitude will allow analysis of the ejection dynamics of the spacecraft using the Smart Nanosatellite Attitude Propagator (SNAP) tool to characterize atmospheric drag for Low Earth Orbit (LEO) CubeSats.